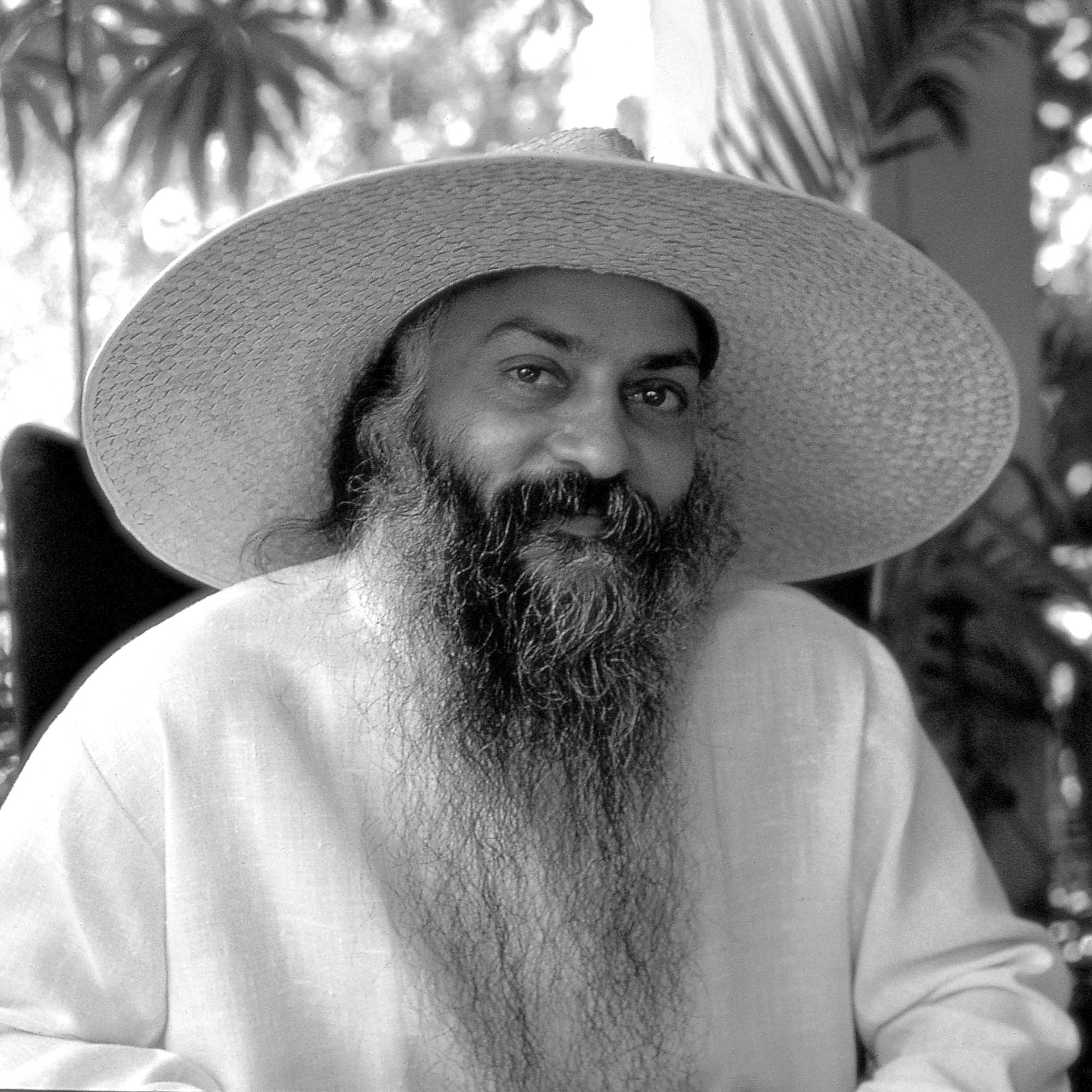
'The most widely owned semiautomatic rifles are “Arms” protected by 2nd Amendment.' Court Decision Upholding Law Making it a Felony to Possess AR-15 Violates the Constitution' - Judge Clarence Thomas
/CLARENCE THOMAS AS UNCLE TOM? FUNKTIONARY REMINDS US, Uncle Tom was killed for withholding information and emancipating others. Sambo is the hanky-head $nigger on which we should look to pull the trigger and drop.
Supreme Court Associate Justice Clarence Thomas showed his hand on Tuesday on the issue of whether AR-15-style rifles are legal. His Second Amendment analysis: They are.
In a brief dissent related to an Illinois ban on the “assault weapon,” Thomas said that the overwhelming popularity of the firearm, coupled with its non-military operation, makes it a clear fit under the Second Amendment. [MORE] Thomas wrote:
Statement of JUSTICE THOMAS.
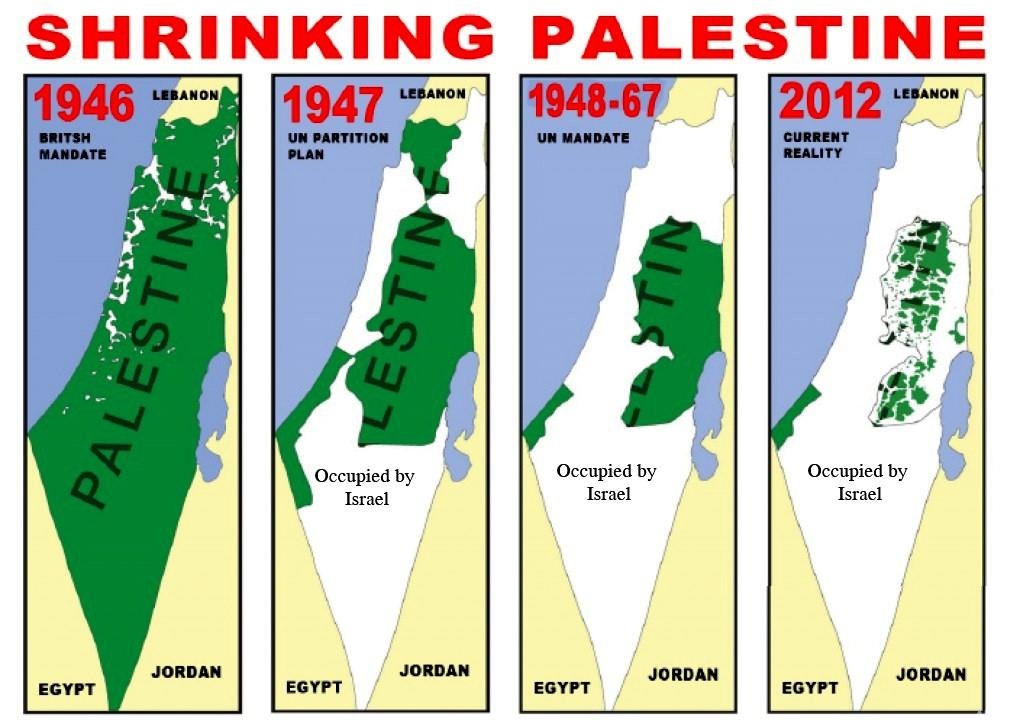
The State of Illinois enacted a law that makes it a felony to possess what Illinois branded “assault weapons,” a term defined to include AR–15s. See Ill. Comp. Stat., ch. 720, §5/24–1.9(a)(1)(J)(ii)(II) (West 2023). “The AR–15 is the most popular semi-automatic rifle” in America and is there- fore undeniably “in common use today.” Heller v. District of Columbia, 670 F.3d 1244, 1287 (CADC 2011) (KAVANAUGH, J., dissenting); see also Garland v. Cargill, 602 U. S. 406, 430–431 (2024) (SOTOMAYOR, J., dissenting) (describing “semiautomatic rifles” such as the AR–15 as “commonly available”). Petitioners sought a preliminary injunction against the enforcement of the law, arguing that the law violates their Second Amendment right to “keep and bear Arms.” The Court of Appeals for the Seventh Cir- cuit rejected petitioners’ request for a preliminary injunc- tion, concluding “that the AR–15 . . . is not protected by the Second Amendment.” Bevis v. Naperville, 85 F. 4th 1175, 1197 (2023). According to the Seventh Circuit, the rifle se- lected by millions of Americans for self-defense and other lawful purposes does not even fall within the scope of the Arms referred to by the Second Amendment. Ibid. This Court is rightly wary of taking cases in an interlocutory pos- ture. But, I hope we will consider the important issues pre- sented by these petitions after the cases reach final judg- ment.
We have never squarely addressed what types of weapons are “Arms” protected by the Second Amendment. To be sure, we explained in District of Columbia v. Heller, 554 U. S. 570 (2008), that the Second Amendment’s protection “extends, prima facie, to all instruments that constitute bearable arms, even those that were not in existence at the time of the founding.” Id., at 582. And, we noted that “the Second Amendment does not protect those weapons not typ- ically possessed by law-abiding citizens for lawful pur- poses,” id., at 625, recognizing “the historical tradition of prohibiting the carrying of dangerous and unusual weap- ons,” id., at 627 (internal quotation marks omitted); see also Caetano v. Massachusetts, 577 U. S. 411, 417–419 (2016) (ALITO, J., concurring in judgment). But, this minimal guidance is far from a comprehensive framework for evalu- ating restrictions on types of weapons, and it leaves open essential questions such as what makes a weapon “beara- ble,” “dangerous,” or “unusual.”
The Seventh Circuit’s decision illustrates why this Court must provide more guidance on which weapons the Second Amendment covers. By contorting what little guidance our precedents provide, the Seventh Circuit concluded that the Second Amendment does not protect “militaristic” weapons. See 85 F. 4th, at 1199. It then tautologically defined “mili- taristic” weapons as those “that may be reserved for mili- tary use.” Id., at 1194. The Seventh Circuit’s contrived “non-militaristic” limitation on the Arms protected by the Second Amendment seems unmoored from both text and history. See Friedman v. Highland Park, 577 U. S. 1039, 1041 (2015) (THOMAS, J., dissenting from denial of certio- rari). And, even on its own terms, the Seventh Circuit’s ap- plication of its definition is nonsensical. See 85 F. 4th, at 1222 (Brennan, J., dissenting) (“The AR–15 is a civilian, not military, weapon. No army in the world uses a service rifle that is only semiautomatic”). In my view, Illinois’ ban is “highly suspect because it broadly prohibits common sem- iautomatic firearms used for lawful purposes.” Friedman, 577 U. S., at 1042 (opinion of THOMAS, J.). It is difficult to see how the Seventh Circuit could have concluded that the most widely owned semiautomatic rifles are not “Arms” protected by the Second Amendment.
These petitions arise from a preliminary injunction, and the Seventh Circuit stressed that its merits analysis was merely “a preliminary look at the subject.” 85 F. 4th, at 1197. But, if the Seventh Circuit ultimately allows Illinois to ban America’s most common civilian rifle, we can—and should—review that decision once the cases reach a final judgment. The Court must not permit “the Seventh Circuit [to] relegat[e] the Second Amendment to a second-class right.” Friedman, 577 U. S., at 1043 (opinion of THOMAS, J.).