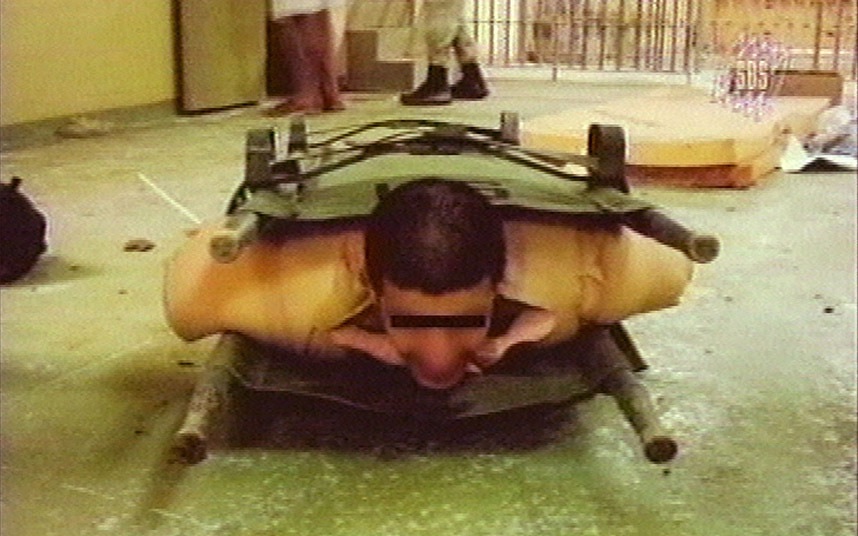
Still No Legal Defense for Failure to Pay Yurugu’s Rent: Many Courts Claim Confusion Over the Eviction Extension, So They Choose to Evict Mostly Non-White Tenants on Behalf of Mostly White Landlords
/IF THERE IS A CONFLICT BETWEEN LAW AND HUMANITY OR BLACK AND WHITE THEN LAW AND/OR WHITE MUST PREVAIL IN THE LEX-ICON [but the procedures will look “fair”] From [HERE] Inside Courtroom 8A of Las Vegas Justice Court last week, the benches were packed with renters and landlords battling over evictions that continued at a brisk pace despite a last minute, two-month extension of the federal protections meant to keep people in their homes.
Vanessa Merryman, 41, was among the tenants ordered to leave her apartment. “I have never been homeless in my life,” she said through tears, slouched on a metal bench outside the courtroom as the scorching Las Vegas sun beat through the windows. She was shellshocked that the court session that upended her life lasted all of 15 minutes. “I do not know what I am going to do,” she said. “It is really scary.”
The federal moratorium on evictions — combined with billions of dollars in rent subsidies — was supposed to avert the scenario of millions of Americans being turned out of their homes after they lost their jobs during the pandemic and were unable to afford their rent.
Yet despite these efforts, many local governments and courts were not sure how to apply the extension, and desperate tenants continued to flood local government websites seeking rental assistance that was usually slow in coming.
“The lay of the land has been confusing at every level, not just to tenants, but also to landlords, court personnel and judges,” said Dana Karni, manager of the Eviction Right to Counsel Project in Houston.
In extending the moratorium last week, the Biden administration hinged it to high local coronavirus infection rates — the idea being that protection was warranted in areas where the virus was surging. Clark County, including Las Vegas, was among hundreds of counties that meet the criterion for high infection rates, but the federal Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines gave some leeway to judges to instead apply state laws, which at times allowed for evictions.
“While the extension of C.D.C. protections is much needed, the confusion that surrounds its existence waters down its impact,” Ms. Karni said.
For many tenants, it was too late anyway. With state moratoriums expiring and the expectation that the federal guidelines would be gone soon, court dockets like those in Las Vegas overflowed with eviction cases. Tenants had to actively file for protection under the C.D.C. measures, but many of them were unaware of that. And as eviction proceedings rolled forward, some landlords won, citing reasons other than nonpayment of rent for seeking to remove tenants.
More than 1.4 million Americans expect to be evicted in the next two months, according to a survey completed by the U.S. Census Bureau in early July. For another 2.2 million people, the prospect is “somewhat likely.”
The areas bracing for the hardest hits are in high-population, high-rent states such as California, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania and Texas, along with other states across the South including Florida, Georgia and South Carolina.
Organizations that advise low-income tenants from Atlanta to Houston to Las Vegas all said that they feared the fallout. “The volume is unlike anything we have ever seen before,” said Bailey Bortolin, the statewide policy director for the Nevada Coalition of Legal Service Providers.
The moratorium is intended to help states buy time to distribute the aid. Congress allocated some $47 billion in rental assistance, but just $3 billion had been distributed by June, according to the Treasury Department. Many county governments, the branch usually designated to process applications, are straining to build systems from scratch to distribute the money even while the tempo of evictions increases.
Georgia has paid out just over $16 million from $989 million in federal rental assistance funds. Florida got $871 million, but has only disbursed $23.2 million.
In Clark County, home to most of Nevada’s population, the CARES Housing Assistance Program has distributed more than $162 million in rent, utilities and mortgage payments to more than 29,500 households since July 2020, but that’s still less than half the state’s full allocation.
Around 50,000 people are behind on rent and could face eviction in Clark County, where the state moratorium expired on June 1, said Justin Jones, a county commissioner.
“It would be devastating if we have that number of people evicted from their homes in the near future,” he said. “The reality is that we do not have anywhere for them to go.” Thousands of homeless people already crowd downtown Las Vegas and elsewhere in the county.
After the state moratorium expired, Nevada implemented a new law pausing evictions so long as the tenant had an application for rental assistance pending.
At the Las Vegas Justice Court, the largest of some 40 courts hearing eviction cases in Nevada, Hearing Master David F. Brown did not allow for much wriggle room. If tenants showed proof that they had applied for rental assistance, they could stay in their homes. If not, or if they had more than a year of late payments, the maximum amount covered by the assistance program, they were usually forced out. Nevada judges tended to emphasize state laws rather than the C.D.C. guidelines.
Dejonae King, 33, held back tears after she lost her eviction appeal. Ms. King was laid off from Walgreens and has been without a job for most of the pandemic. She had not paid the $253 weekly rent on her one-bedroom apartment since July 2020. “I thought the rules would protect me,” she said.
Ms. Merryman had managed to pay $10,000 in rent from government subsidies last year, but she lost her business and her boyfriend’s lengthy struggle with Covid interrupted her efforts to apply for more. It took her four months to reset her lost password for the website to apply for government payments.
Meanwhile, many landlords are caught in a vicious cycle, constantly in court but never quite made whole, said Susy Vasquez, executive director of the Nevada State Apartment Association, the largest organization for landlords. [MORE]