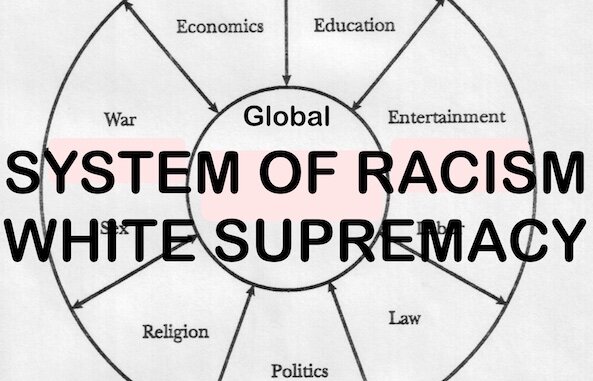
Government and Private Sector Preying on the Poor
/From [HERE] Individually the poor are not too tempting to thieves, for obvious reasons. Mug a banker and you might score a wallet containing a month’s rent. Mug a janitor and you will be lucky to get away with bus fare to flee the crime scene. But as Business Week helpfully pointed out in 2007, the poor in aggregate provide a juicy target for anyone depraved enough to make a business of stealing from them.
The trick is to rob them in ways that are systematic, impersonal, and almost impossible to trace to individual perpetrators. Employers, for example, can simply program their computers to shave a few dollars off each paycheck, or they can require workers to show up 30 minutes or more before the time clock starts ticking.
Lenders, including major credit companies as well as payday lenders, have taken over the traditional role of the street-corner loan shark, charging the poor insanely high rates of interest. When supplemented with late fees (themselves subject to interest), the resulting effective interest rate can be as high as 600% a year, which is perfectly legal in many states.
It’s not just the private sector that’s preying on the poor. Local governments are discovering that they can partially make up for declining tax revenues through fines, fees, and other costs imposed on indigent defendants, often for crimes no more dastardly than driving with a suspended license. And if that seems like an inefficient way to make money, given the high cost of locking people up, a growing number of jurisdictions have taken to charging defendants for their court costs and even the price of occupying a jail cell.
The poster case for government persecution of the down-and-out would have to be Edwina Nowlin, a homeless Michigan woman who was jailed in 2009 for failing to pay $104 a month to cover the room-and-board charges for her 16-year-old son’s incarceration. When she received a back paycheck, she thought it would allow her to pay for her son’s jail stay. Instead, it was confiscated and applied to the cost of her own incarceration.
Government Joins the Looters of the Poor
You might think that policymakers would take a keen interest in the amounts that are stolen, coerced, or extorted from the poor, but there are no official efforts to track such figures. Instead, we have to turn to independent investigators, like Kim Bobo, author of Wage Theft in America, who estimates that wage theft nets employers at least $100 billion a year and possibly twice that. As for the profits extracted by the lending industry, Gary Rivlin, who wrote Broke USA: From Pawnshops to Poverty, Inc. -- How the Working Poor Became Big Business, says the poor pay an effective surcharge of about $30 billion a year for the financial products they consume and more than twice that if you include subprime credit cards, subprime auto loans, and subprime mortgages.
These are not, of course, trivial amounts. They are on the same order of magnitude as major public programs for the poor. The government distributes about $55 billion a year, for example, through the largest single cash-transfer program for the poor, the Earned Income Tax Credit; at the same time, employers are siphoning off twice that amount, if not more, through wage theft.
And while government generally turns a blind eye to the tens of billions of dollars in exorbitant interest that businesses charge the poor, it is notably chary with public benefits for the poor. Temporary Assistance to Needy Families, for example, our sole remaining nationwide welfare program, gets only $26 billion a year in state and federal funds. The impression is left of a public sector that’s gone totally schizoid: on the one hand, offering safety-net programs for the poor; on the other, enabling large-scale private sector theft from the very people it is supposedly trying to help.
At the local level though, government is increasingly opting to join in the looting. In 2009, a year into the Great Recession, I first started hearing complaints from community organizers about ever more aggressive levels of law enforcement in low-income areas. Flick a cigarette butt and get arrested for littering; empty your pockets for an officer conducting a stop-and-frisk operation and get cuffed for a few flakes of marijuana. Each of these offenses can result, at a minimum, in a three-figure fine.
And the number of possible criminal offenses leading to jail and/or fines has been multiplying recklessly. All across the country -- from California and Texas to Pennsylvania -- counties and municipalities have been toughening laws against truancy and ratcheting up enforcement, sometimes going so far as to handcuff children found on the streets during school hours. In New York City, it’s now a crime to put your feet up on a subway seat, even if the rest of the car is empty, and a South Carolina woman spent six days in jail when she was unable to pay a $480 fine for the crime of having a “messy yard.” Some cities -- most recently, Houston and Philadelphia -- have made it a crime to share food with indigent people in public places.
Being poor itself is not yet a crime, but in at least a third of the states, being in debt can now land you in jail. If a creditor like a landlord or credit card company has a court summons issued for you and you fail to show up on your appointed court date, a warrant will be issued for your arrest. And it is easy enough to miss a court summons, which may have been delivered to the wrong address or, in the case of some bottom-feeding bill collectors, simply tossed in the garbage -- a practice so common that the industry even has a term for it: “sewer service.” In a sequence that National Public Radio reports is “increasingly common,” a person is stopped for some minor traffic offense -- having a noisy muffler, say, or broken brake light -- at which point the officer discovers the warrant and the unwitting offender is whisked off to jail.
Local Governments as Predators
Each of these crimes, neo-crimes, and pseudo-crimes carries financial penalties as well as the threat of jail time, but the amount of money thus extracted from the poor is fiendishly hard to pin down. No central agency tracks law enforcement at the local level, and local records can be almost willfully sketchy.
According to one of the few recent nationwide estimates, from the National Association of Criminal Defense Lawyers, 10.5 million misdemeanors were committed in 2006. No one would risk estimating the average financial penalty for a misdemeanor, although the experts I interviewed all affirmed that the amount is typically in the “hundreds of dollars.” If we take an extremely lowball $200 per misdemeanor, and bear in mind that 80%-90% of criminal offenses are committed by people who are officially indigent, then local governments are using law enforcement to extract, or attempt to extract, at least $2 billion a year from the poor.
And that is only a small fraction of what governments would like to collect from the poor. Katherine Beckett, a sociologist at the University of Washington, estimates that “deadbeat dads” (and moms) owe $105 billion in back child-support payments, about half of which is owed to state governments as reimbursement for prior welfare payments made to the children. Yes, parents have a moral obligation to their children, but the great majority of child-support debtors are indigent.
Attempts to collect from the already-poor can be vicious and often, one would think, self-defeating. Most states confiscate the drivers’ licenses of people owing child support, virtually guaranteeing that they will not be able to work. Michigan just started suspending the drivers’ licenses of people who owe money for parking tickets. Las Cruces, New Mexico, just passed a law that punishes people who owe overdue traffic fines by cutting off their water, gas, and sewage.
Once a person falls into the clutches of the criminal justice system, we encounter the kind of slapstick sadism familiar to viewers of Wipeout. Many courts impose fees without any determination of whether the offender is able to pay, and the privilege of having a payment plan will itself cost money.
In a study of 15 states, the Brennan Center for Justice at New York University found 14 of them contained jurisdictions that charge a lump-sum “poverty penalty” of up to $300 for those who cannot pay their fees and fines, plus late fees and “collection fees” for those who need to pay over time. If any jail time is imposed, that too may cost money, as the hapless Edwina Nowlin discovered, and the costs of parole and probation are increasingly being passed along to the offender.
The predatory activities of local governments give new meaning to that tired phrase “the cycle of poverty.” Poor people are more far more likely than the affluent to get into trouble with the law, either by failing to pay parking fines or by incurring the wrath of a private-sector creditor like a landlord or a hospital.
Once you have been deemed a criminal, you can pretty much kiss your remaining assets goodbye. Not only will you face the aforementioned court costs, but you’ll have a hard time ever finding a job again once you’ve acquired a criminal record. And then of course, the poorer you become, the more likely you are to get in fresh trouble with the law, making this less like a “cycle” and more like the waterslide to hell. The further you descend, the faster you fall -- until you eventually end up on the streets and get busted for an offense like urinating in public or sleeping on a sidewalk.
I could propose all kinds of policies to curb the ongoing predation on the poor. Limits on usury should be reinstated. Theft should be taken seriously even when it’s committed by millionaire employers. No one should be incarcerated for debt or squeezed for money they have no chance of getting their hands on. These are no-brainers, and should take precedence over any long term talk about generating jobs or strengthening the safety net. Before we can “do something” for the poor, there are some things we need to stop doing to them.