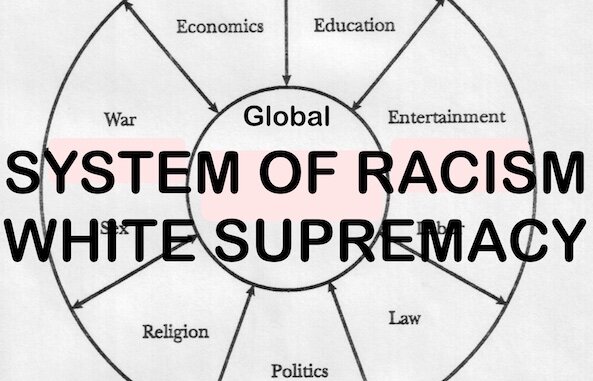
White Over Black System of Unequal Power: In D.C. White Families Are 81 Times Richer Than Black Ones
/ From [The Atlantic] The wealth discrepancy between blacks and whites is one of the most stark examples of inequality in America. White American families have, on average, around $142,000 in savings and assets, minus debt. Black families’, meanwhile, amounted to only $11,000, according to a 2014 Pew Research study. The gulf between black and white wealth is the worst it has been since the 1980s. Put differently, an average white family has 13 times the wealth of an average black family.
From [The Atlantic] The wealth discrepancy between blacks and whites is one of the most stark examples of inequality in America. White American families have, on average, around $142,000 in savings and assets, minus debt. Black families’, meanwhile, amounted to only $11,000, according to a 2014 Pew Research study. The gulf between black and white wealth is the worst it has been since the 1980s. Put differently, an average white family has 13 times the wealth of an average black family.
But as though the median numbers for the country as a whole weren’t bad enough, things look much worse in America’s cities, according to a new paper from the Urban institute—even cities such as D.C. where the prevalence of public-sector jobs, a large black population, and a high share of black business owners might make it seem like a place that black families could thrive. But in Washington D.C., the median white family has a staggering 81 times as much wealth as the median black family.
D.C. is not an outlier: In general, urban areas have much more severe racial inequalities, in part because of the concentration of white wealthy people, and the fact that their wealth has not “trickled down” to poor and middle-class black families. According to a 2015 National Asset Scorecard for Communities of Colors, D.C.’s racial wealth gap falls just behind Los Angeles’s, where median wealth for whites was closer to 89 times as much as blacks’. In Miami it was 30 times as high; in Tulsa, 18 times.
Darrick Hamilton, a professor at the New School and one of the authors of the Urban Institute’s study—along with fellow economists Kilolo Kijakazi, Rachel Marie Brooks Atkins, Mark Paul, Anne Price, and William A. Darity Jr.—says that while many ethnic groups might do poorly in one city and thrive in another, that’s not the case for black Americans. “No matter what the geographical context is, black Americans are a low-wealth group,” he told me. “I think the disparities are going to be dramatic wherever we look.”
Hamilton says that while the statistics about magnitude are useful for distilling the gap in balance sheets, they do little to capture what the wealth gap means for black families. In practice, less wealth means diminished access to the education and opportunities that help many Americans reach the middle class. Less wealth decreases opportunities for savings, homeownership, and economic security. And limited wealth accumulation also means that parents and grandparents have little to pass along to the next generation—from paying for school to helping with down payments—which dampens opportunities for intergenerational mobility.
D.C.’s wealth inequality stems from a combination of factors. According to the study, homeownership plays a significant role: Whites living in the District are much more likely than blacks to own homes—something that’s true around the country. In the District, whites with less than a high school education were more likely to own their homes than blacks at any education level, even those with college degrees. And for those who do own their own place, home values for black owners were around $250,000, about 30 percent less than the average value for white owners. Blacks in the District have a much higher unemployment rate, lower education rates, and are much more likely to have received a subprime mortgage.
The District’s racial wealth divide has old and deep origins in centuries of racist policies. The authors highlight a few in particular: the “black codes” of the 1840s, which prevented black people from owning successful stores or working in certain professions; the return of land in the District to the South in the 1870s, which decreased opportunities for ownership among newly freed blacks; the demolition of Barry Farms—a black enclave founded by freed blacks—in the 1940s to make way for public housing and highway projects; the wave of “urban renewal” projects that swept out black businesses and residents in the 1960s and 70s. The effects of these policies have never been adequately dealt with. “Black people in D.C. have faced more than two centuries of deliberately constructed barriers to wealth building, and some of the highest barriers were embedded by design in law,” the study says.
In the present day, an influx of whiter, wealthier residents is pushing older black residents out. Though property values are increasing, which in theory helps black homeowners, many aren’t able to cash in: Blacks are less likely to own homes in the first place, and many who did were saddled with dangerous subprime loans, and lost their homes to foreclosure during the mortgage crisis. Those who still own their homes tend to owe higher amounts on their mortgages and are more likely to be underwater, making selling much less lucrative proposition than it is for their white counterparts.
One of the main takeaways of the research is that narratives about wealth creation—such as education and hard work as the key to success, or homeownership as a starting point for asset-building—leave out the important truth that wealth begets wealth. “Homeownership is an attribute of wealth,” Hamilton says. “It is wealth in the first place that allows them to have that down payment to generate wealth from homeownership.” Both in the District and nationally, black Americans lag behind in homeownership, and are less likely to own other assets that passively create wealth over time, such as investments or trusts. And they’re much less likely to have inherited wealth from their parents, or family members, or to have received money for a downpayment or to defray the cost of college. [MORE]